In sum, the outlook for a resolution to the US-China trade dispute is very cloudy, and a slew of tit-for-tat tariffs have already been applied by both countries, and there are many more scheduled by year-end.
President Trump continues down two parallel paths, as we see it. The first path is the effort to reach a comprehensive agreement that addresses American grievances related to forced technology transfers, IP theft, fair market access, and Chinese state subsidies to domestic businesses. Assumedly, a partial deal would be met with the removal of some, but not all tariffs. The second path is the formation of a US trading sphere so as to create two international trading spheres with the US and China at the center of each.
Today, the prospects for a comprehensive trade deal with China are poor, while two distinct international trading spheres appear to be forming.
The Trump Administration has agreed to a revised US-Korea free trade agreement (September 2018) and the new US-Mexico-Canada Agreement or “USMCA” (June 2019), which replaced NAFTA. Furthermore, the White House is working on new trade agreements with Japan, the European Union, and the United Kingdom.
It appears that a deal with Japan is getting closer to being sealed as President Trump and Prime Minister Shinzo Abe agreed to “core principles” at the recent G7 meeting. It’s possible that the deal will be finalized within the next 1-2 months. At the same time, Trump and Prime Minister Boris Johnson have spoken positively about a major US-UK deal if Brexit happens. As for a US-EU deal, Trump struck an upbeat tone at the G7 meeting, saying “We’re very close to maybe making a deal with the EU because they don’t want tariffs.”[v] With this new US-centric trading sphere taking shape, it may explain why Trump seemed so upbeat about the G7 meeting.
Given the current circumstance, we expect President Trump to keep up the significant pressure on China to force into a more reciprocal trading relationship, and the path is unlikely to be smooth.
First, Trump could still apply more economic pressure possibly by raising tariffs even higher, utilizing the Emergency Economic Powers Act of 1977 to force US companies to divest from China, or even sanctioning Chinese companies or officials suspected of human rights violations.
Secondly, as the complex negotiations continue, it’s likely we’ll hear more mixed signals from President Trump. Asked by reporters at the G7 summit about his seemingly back-and-forth and changing statements on subjects such as President Xi and Iran, the President said, “Sorry, it’s the way I negotiate… It’s done very well for me over the years, and it’s doing even better for the country.”[vi]
Bottom Line: We believe President Trump’s negotiating strategy is becoming increasingly clear, and there are more levers he can pull to pressure China to concede to US demands. Given how much further Trump can go as well as the weak Chinese economy today, the odds are rising in our view that Chinese officials will compromise on at least some major demands in the coming year. A comprehensive deal, however, is still a long shot – as that arguably would entail a wholesale reformation of the Chinese economic system.
Fed Policy: There are three more FOMC meetings before year-end, with the next one scheduled for September 17-18. At that meeting, federal funds futures are currently implying a nearly 96% probability of a 25 basis point rate cut, and 4% probability of a 50 basis point cut -- according to the CME Fedwatch Tool.
Arguably, the Fed must cut interest rates aggressively, and soon. The Fed is hostage to the market, trade negotiations, and other major macro uncertainties in the world today that are inhibiting risk-taking and production and thus slowing global economic activity. The inverted Treasury curve is another indication of the significant pressure on the Fed to cut interest rates. For example, the 3-month/2-year Treasury spread is approximately -47 basis points today, according to the St. Louis Federal Reserve. From our perspective, this implies that the market believes the funds rate is at least 50 basis points too high at the moment.
Is the inverted yield curve a signal of a looming recession? We believe that it’s an ominous signal, given its track record for preceding many recessions, and an indication of central bank error. But recession isn’t guaranteed. It’s still possible that aggressive rate cuts by the Fed and more clarity and resolution to many other macro uncertainty could re-ignite animal spirits and keep the United States from recession.
Notably, former New York Federal Reserve President William Dudley penned a highly controversial Bloomberg oped on August 27, in which he expressed a desire for the Fed to withhold interest rate reductions in order to not “bail out an administration that keeps making bad choices on trade policy”.[vii] It also appeared that Dudley went even further to suggest that the Fed pursue monetary policy into the November 2020 elections in a manner that prevented President Trump’s reelection.
But Dudley’s oped may backfire. It seems that the popular response to his oped has been critical, and ironically, may in fact turn the tables and force the Fed to prove that it isn’t acting in an “anti-Trump” manner by withholding rate cuts, but is purely economically motivated and therefore will reduce interest rates aggressively during the coming months.
ECB Policy: At its next monetary policy meeting on September 12, it looks like the ECB will be meaningfully dovish, at least according to Olli Rehn, a member of the ECB’s rate-setting committee and governor of Finland’s central bank.
On Thursday, August 15, Rehn said, “When you’re working with financial markets, it’s often better to overshoot than undershoot, and better to have a very strong package of policy measures than to tinker.”[viii]
We believe the ECB will lower its benchmark overnight rate by 10-20 basis points from negative 0.40% currently; announce new bond purchases (“quantitative easing”); and favorably adjust loan terms for EU banks.
As we indicated last month, the sharpest slowdown in growth globally may be occurring in Europe. It looks like the ECB is preparing to pull out the figurative monetary bazooka in a few weeks.
Bottom Line: We expect the Federal Reserve and European Central Bank to continue moving dovishly, and if conditions deteriorate further, they will need to do so in a big way – such as a 50 basis point cut at an upcoming FOMC meeting.
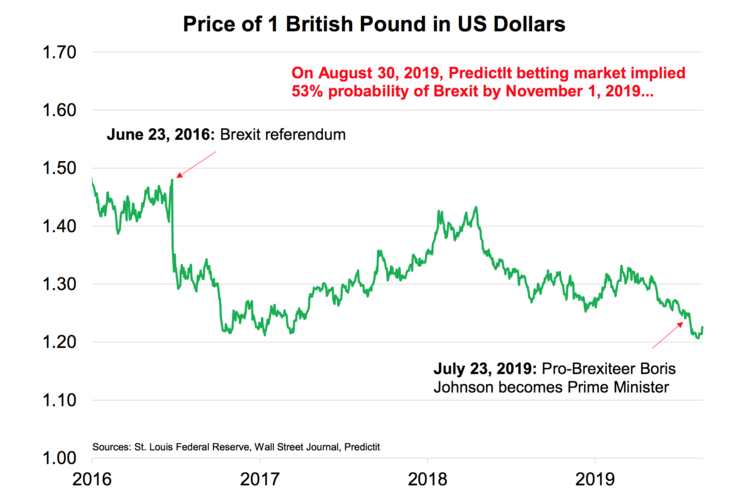
Brexit: Prime Minister Boris Johnson has famously said that he’ll achieve Brexit by the October 31 deadline “do or die”. To that end, he shocked the world on August 28 by announcing that his Parliament will be suspended sometime between September 9-12, thanks to Queen Elizabeth II’s approval. Parliament will recommence after the Queen’s speech on October 14.[ix] This will give anti-Brexiters in the legislature little time to stop a no-deal Brexit by its lawfully mandated deadline.
Interestingly, the EU Council Meeting is scheduled to take place October 17-18. It appears that there are two possible scenarios emerging here: 1) if Johnson returns with a new Brexit deal, then he’ll hope to ram it through Parliament with less than two weeks to the deadline; or 2) if Johnson does not return with a new deal, then a no-deal Brexit may automatically occur by the deadline.
In sum, the probability of Brexit has increased substantially thanks to Johnson’s crafty political maneuvering. On August 28, the Predicit market for Brexit occurring by November 1 was 58 cents on the dollar; whereas the day before, the contract traded at 48 cents.[x]